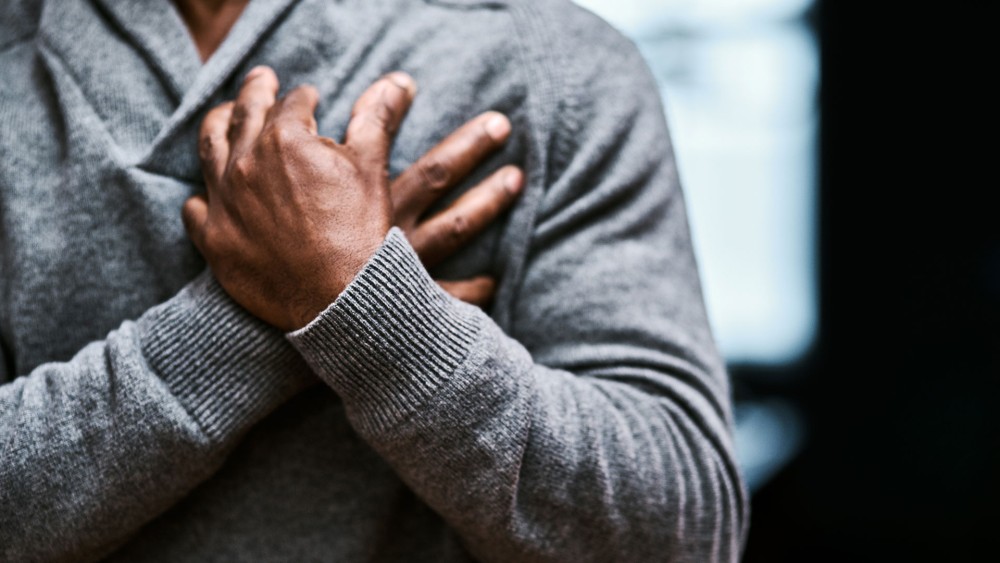

What is the difference between Heart Attack and Cardiac Arrest?
A heart attack and cardiac arrest are two different medical emergencies that can occur when the heart is not functioning properly. While they are related, it's important to understand the differences between the two conditions.
A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when there is a blockage in one or more of the coronary arteries, which are the blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart. This blockage can cause a portion of the heart muscle to die, leading to chest pain, shortness of breath, and other symptoms. Heart attacks can be treated with medications to dissolve the blockage and with procedures to open the blocked artery, such as angioplasty or coronary artery bypass surgery.
Cardiac arrest, on the other hand, occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating. This can be caused by a number of factors, including a heart attack, electrical problems with the heart, or an external event like drowning or electrocution. Cardiac arrest is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention, as the lack of blood flow to the body can cause serious damage to the brain and other organs. Cardiac arrest is typically treated with CPR and defibrillation, which can restore a normal heart rhythm.
While a heart attack can lead to cardiac arrest, it's essential to understand that they are two different medical emergencies.
If you or someone you know is experiencing a heart attack or cardiac arrest symptoms, it's important to seek medical attention immediately. Quick treatment can save lives and reduce the risk of long-term complications.




Add a Comment